Related Articles

IT Outsourcing
RSK BSL Tech Team
May 23, 2025
|
|

AI Tech Solutions
RSK BSL Tech Team
May 19, 2025
|
|

Software Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
May 16, 2025
|
|

Software Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
May 13, 2025
|
|

IT Outsourcing
RSK BSL Tech Team
May 4, 2025
|
|

Mobile Application Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 30, 2025
|
|
Software Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 27, 2025
|
|

Hire resources
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 24, 2025
|
|

Software Development
Praveen Joshi
April 20, 2025
|
|

Artificial Intelligence
Praveen Joshi
April 17, 2025
|
|

Pen Testing
Praveen Joshi
April 15, 2025
|
|

AI Tech Solutions
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 14, 2025
|
|

Software Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 9, 2025
|
|

Pen Testing
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 7, 2025
|
|

Software Development
RSK BSL Tech Team
April 3, 2025
|
|
Cloud Application
RSK BSL Tech Team
March 31, 2025
|
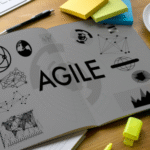
advantages of integrating cloud computing into custom software solutions
In recent years, the adoption of cloud computing among UK enterprises has surged, with over 88% of businesses now utilising cloud services to some extent. This growing trend highlights the significant advantages that cloud computing offers in terms of flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. This blog aims to explore the benefits of integrating cloud computing into custom software development UK, demonstrating how it can enhance business operations and drive innovation.
Understanding Cloud Computing
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is the internet-based delivery of computer services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics (“the cloud”). This concept eliminates the requirement for on-premises infrastructure by enabling organisations to access and use these resources as needed.
Core Components of Cloud Computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualised computing resources over the internet. IaaS allows businesses to rent IT infrastructure—servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, and operating systems—from a cloud provider on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS): Uses the Internet to deliver hardware and software tools. PaaS is intended to handle the entire web application lifecycle: development, testing, deployment, management, and updates.
- Software as a Service (SaaS): Software programs are delivered over the internet via subscription. SaaS providers host and administer the software application and underlying infrastructure and perform maintenance tasks like software upgrades and security patches.
Relevance to Custom Software Solutions:
Cloud computing is particularly relevant for custom software solutions due to its ability to provide scalable, flexible, and cost-effective resources. By leveraging cloud services, businesses can develop and deploy custom software that meets their specific needs without the constraints of traditional IT infrastructure. This approach not only reduces costs but also accelerates development timelines and enhances the overall agility of the business.
Cost Efficiency
1.Reduced Infrastructure Costs:
One of the most significant advantages of integrating cloud computing into custom software solutions is the elimination of expensive on-premises hardware. Traditional IT infrastructure requires substantial upfront investment in servers, storage devices, and networking equipment. In contrast, cloud computing allows businesses to access these resources over the internet, reducing the need for physical hardware and associated costs.
2.Pay-as-You-Go Model:
Cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which means businesses only pay for the resources they actually use. This model provides significant cost benefits, as it eliminates the need for over-provisioning and allows companies to scale their usage based on demand. For example, during peak periods, businesses can increase their resource allocation, and during off-peak times, they can scale down, ensuring cost efficiency.
3.Operational Savings:
Beyond infrastructure costs, cloud computing also leads to operational savings. Maintenance of on-premises hardware can be costly and time-consuming, requiring regular updates, repairs, and replacements. Cloud service providers handle all maintenance tasks, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic initiatives. Additionally, cloud solutions reduce energy consumption, as businesses no longer need to power and cool large data centres, further lowering operational expenses.
Scalability and Flexibility
·On-Demand Resources:
Cloud computing provides exceptional scalability, allowing firms to increase or decrease resources based on demand. This flexibility is particularly beneficial for custom software solutions, which may experience varying levels of usage. For instance, an e-commerce platform might see a surge in traffic during holiday seasons, requiring additional computing power. With cloud computing, businesses can quickly and easily adjust their resource allocation to meet these demands without any disruption to service.
·Flexibility:
Cloud solutions can be customised to meet specific business needs, providing a tailored approach to software development. This customisation extends to various aspects, including storage capacity, processing power, and software configurations. Moreover, cloud computing supports remote work and collaboration by enabling access to software and data from anywhere with an internet connection. This flexibility enhances productivity and allows teams to collaborate in real-time, regardless of their physical location.
Improved Collaboration and Accessibility
·Remote Access:
One of the most prominent advantages of cloud computing is the ability to access applications and data from any location with an internet connection. By leveraging cloud-based solutions, employees can access the tools and information they need to perform their tasks from any location, whether they are working from home, traveling, or at a client site. This flexibility not only supports remote work but also enhances productivity by ensuring that team members have uninterrupted access to essential resources.
·Real-Time Collaboration:
Cloud-based tools facilitate real-time collaboration among team members, regardless of their physical location. Features such as shared documents, collaborative editing, and instant messaging enable teams to work together seamlessly.
Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
·Data Backup:
Regular data backups are crucial for protecting against data loss due to hardware failures, cyberattacks, or other unforeseen events. Cloud computing ensures that data is backed up across multiple locations, providing a robust safeguard against data loss. Cloud service providers typically offer automated backup solutions that regularly save copies of data to secure, geographically dispersed data centres. This redundancy ensures that even if one data centre experiences an issue, the data remains safe and accessible from another location.
·Quick Recovery:
In the event of data loss or system failures, cloud solutions enable quick recovery, ensuring business continuity. Cloud service providers offer disaster recovery services that allow businesses to restore their data and systems rapidly. These services often include features such as snapshot backups, which capture the state of a system at a specific point in time, and failover mechanisms, which automatically switch to a backup system in case of a failure. By leveraging these capabilities, businesses can minimise downtime and maintain operations even in the face of disruptions.
Innovation and Competitive Advantage
Access to Latest Technologies:
- AI and ML: Cloud platforms offer AI and machine learning services for developing intelligent applications and automating processes.
- Big Data Analytics: Tools for processing and analysing large datasets, driving data-driven decision-making.
Competitive Edge:
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Personalised recommendations and automated customer support.
- Operational Optimisation: Identifying trends and optimising operations for better efficiency.
- Market Opportunities: Uncovering new opportunities through data insights.
Real-world examples
1.RSK Business Solutions
It developed the CompassEnviro Suite, a project management and environmental compliance platform. By leveraging cloud computing, RSK Business solutions ensured the platform could scale to meet various client needs, providing real-time risk assessments and legal registry tracking. This integration resulted in significant operational efficiencies and enhanced data security.
2.Emvigo Technologies
It created a custom software solution for a healthcare provider. They integrated advanced encryption techniques and conducted regular security audits to ensure compliance with GDPR and HIPAA regulations. This approach improved data protection and regulatory adherence, demonstrating the effectiveness of cloud computing in enhancing security and compliance.
3.Arrow ECS UK
It facilitated cloud migration and modernisation for various UK enterprises. This project enhanced operational efficiency, reduced infrastructure costs, improved scalability, and provided access to advanced cloud technologies. By adopting cloud solutions, Arrow ECS UK helped businesses achieve significant cost savings and operational improvements.
Challenges and Solutions
Potential Challenges:
- Data Migration: Moving existing data to the cloud can be complex and time-consuming.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensuring seamless integration with legacy systems and applications.
- Security Concerns: Protecting sensitive data and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Downtime and Disruptions: Minimising downtime during the transition to cloud services.
- Cost Management: Controlling costs associated with cloud services and avoiding unexpected expenses.
- Vendor Lock-In: Avoiding dependency on a single cloud provider and ensuring flexibility.
Solutions:
- Experienced Cloud Service Providers: Partner with providers who have a proven track record in data migration and integration.
- Robust Security Measures: Implement encryption, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
- Hybrid Solutions: Use a hybrid approach to gradually transition to the cloud while maintaining critical on-premises systems.
- Clear Migration Plan: Develop a detailed migration plan with timelines, milestones, and contingency measures.
- Cost Monitoring Tools: Utilise tools to monitor and manage cloud service costs effectively.
- Multi-Cloud Strategy: Adopt a multi-cloud strategy to avoid vendor lock-in and increase flexibility.
Conclusion
Integrating cloud computing into custom software solutions offers numerous advantages for UK enterprises, including cost efficiency, scalability, enhanced security, and improved collaboration. By working with experienced cloud service providers and implementing robust security measures, businesses can overcome these challenges and fully leverage the benefits of cloud computing. This approach not only drives innovation but also ensures that companies remain agile and competitive in a rapidly evolving digital landscape. For those seeking to enhance their operations, partnering with a provider of custom software development services can be a strategic move towards achieving these goals.
RSK BSL Tech Team
 Share
Share Post
Post Tweet
Tweet Copy
Copy


